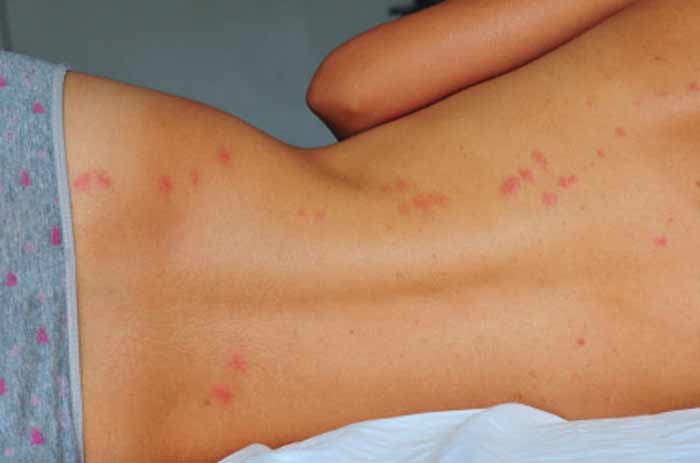
Different people have different reaction to bites from bed bugs. The effect of their bite can spread easily to the blood within a very short time. In this article, find out whether bed bugs have a potential to make you sick. Further, the article tries to explain the dangers that can come from bed bugs and the bites.
Table of Contents
Can they make you sick?
There are a number of studies which try to explain whether or not bed bugs have an impact on the health of an individual. Here are some of them:
According to the study by Center for Disease Control and Prevention, bed bugs are not known to cause any disease. They are just a source of annoyance because their bites cause a lot of itchiness and irritation.
Other times, the itchiness and irritation could prompt you to continuously scratch and this could predispose you to secondary infection. There can also be allergic reactions from the bites that need medication.[1]
According to the Orkin website, bed bugs are known carriers of disease organisms but are not actively involved in causing diseases.
There are studies that suggest that bed bugs can be at the focal point in the spread of leprosy, brucellosis and oriental sores. However, this information is scanty and not conclusive.
The lead cause of the disease spread is the onset of secondary infections. Further, a depressed immune system could make you more susceptible to other infections after the bed bug bite.[2]
New developments from the study from the Center for Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics show that bed bugs could carry the parasite Trypanosome cruzi, a vector that is known to cause Chagas disease; which is one of the deadliest and most prevalent diseases among the Americans.
There was a similar study in support of this by Michael Levy, PhD, an assistant professor in the department of Biostatics and Epidemiology at University Pennsylvania in the school of Medicine. They investigated and found out that bed bugs carry and transmit T. cruzi.[3]
How are bed bugs dangerous?
There are a number of responses that your body can show when you are bitten by bed bugs. It could either be sensitivity or allergic reactions. There are other cases when other complications set in.
Allergies from bites
This is a reaction that is likely to occur shortly after the bite. You can show sensitivity in different ways when compared to other people.
This is because of the chemical that the bugs introduce into your body when they bite. The sensitivity can make you scratch your body and this results in a lot of itchiness on your skin.
This in the course of time could expose you to other potential infections that eventually would lead to scar formation. You should see you doctor as soon as you realize the situation is becoming unbearable.
They present in the form of a rash that may not be contagious. The allergic reactions in real sense are unique from one individual to the other. There are people who notice these while others might just not notice the bites. It is so easy for you to confuse these bites with mosquito bites and you should therefore be careful to distinguish.
The allergic reactions could be just mild or even severe. When it occurs, there is an occurrence of rashes on your skin, itching and a lot of inflammation. The case can be so severe to an extent that you will be forced to treat using antihistamines, corticosteroids and anti-itch ointments. This is according to the Michigan Department of Community Health.
Anemia
There are some cases where there is a possibility of anemia setting in as a result of heavy infestation and dangerous bites from the bed bugs.
According to the Canadian Medical Association Journal in 2009, there was a case where there was a likely link between bed bug infestation and anemia.
There was a case that revealed there was an individual who was a man who suffered iron deficiency and upon investigation, it was discovered that there was a lot of infestation of bed bugs in the house of the man. The conclusion from the investigation was that the case is only in extreme infestation.[4]
Bed bugs can worsen respiratory conditions
When you have a respiratory problem, the bites by bed bugs can make this more dangerous. As the bugs grow, they shed their outer layers of their skins and casings. When all these dry, they can after sometime become airborne.
When you breathe in the chaff, you are most likely to get a respiratory block and in the event of asthma, then the condition can only get worse.
Secondary infections
When you scratch the bitten spots, you open up the pores on your skin. After a while, the bacteria and other microorganisms get an opportunity to penetrate and terrorize the cells.
The microbes multiply and then cause a lot of harm to your body. Your doctor will always give you the medication to use to remedy this.
They may lead to a disturbed life
Apart from the above effects the bugs have on your body, they generally would be a nuisance and interference to the flow of your life.
They can make you lack sleep and with this, your health status is likely to deteriorate to a great extent. Further, the menace can cost you a lot of money trying to treat the irritations and the itchiness that come by.
Inasmuch as this could look like an issue of convenience, it could be dangerous if after a while, the bites affect the way you discharge your duties at the place of work.
Bed bugs could even terrorize you to even as far as your car and as a result, this could cause a lot of discomfort and even accidents in the long run. Be sure to ensure that they do not take away your attention as it would be detrimental. Always ensure you keep watch to detect them as soon as they appear.
Further Reading
- Bed Bug Sniffing Dogs-How they smell, Sense, Roscoe, Breeds & Cost
- What are Bed Bugs? Names in other Languages
- Where do Bed Bugs come from? Causes, how you get them & Start
- How to Kill/Get Rid of Bed Bugs Fast Yourself Naturally for Good
- Bed Bugs in Hair Symptoms, Pictures & Get rid
- Types of Bed Bugs
- Bed Bug Poop/Droppings-How it looks like, Pictures +Identification
- Bed Bug Shells, Cast Skin & Exoskeleton
- Can you See Bed Bugs with the Naked eye? Pictures, Size, Color & Anatomy
- Dust Mite vs Bed Bug Bites
- Bed Bug life cycle-Eggs, Baby(Nymph) to Adult Stages & Pictures
- How to Detect Bed Bugs-Detectors, Light & Verifi Reviews
- How to know if Bed Bugs are gone after Treatment & what to do
- Will Bleach Kill Bed Bugs-How does it work?
- Best Bed Bugs Traps- DIY Homemade, Co2, Yeast + Reviews
- How to Deal with Bed Bugs in your Car
- Bed Bugs in Couch-Covers, Signs & How to Get rid
- How to Kill Bed Bugs with Steam: Best Steamers & Guide + Tips
- Does Alcohol Kill Bed Bugs? Rubbing, Isopropyl & Percentage
- How Long do Bed Bug Bites Last, Take to Appear, Go Away & Heal
- Natural Predator of Bed Bugs-What Insects/Bugs eat Bed Bugs?
- Can Bed Bugs Live in TVs & Other Electronics? How to get them out
- Do Bed Bug Bites Itch or Hurt?
- Bed Bug Interceptor-How it works, DIY & Reviews
- What do Bed Bug Bites look like? Pictures & Identification Steps
- What Attracts Bed Bugs & things they Hate /Dislike Most
- Can Bed Bugs make you Sick? How are they Dangerous?
- Can Bed Bugs Fly-Do they have Wings-How Far can they Travel
- Diatomaceous Earth for Bed Bugs-How to Use & Best Reviews
- DIY Bed Bug Heat Treatment: Success Rate,Temperature Chart, Preparation & Reviews
- Does Vinegar Kill Bed Bugs? Can it be Used for Bites?
- How to Get Rid of Bed Bugs on Mattress- Best Covers, Protectors & Encasement Reviews
- Can Bed Bugs live on or Bite Dogs & Cats (Pets)?
- Bugs that look like Bed Bugs-Beetles & Others that Resemble or Mistaken
- Bed Bug Bombs-Do Foggers work? Effectiveness & Reviews
- Bed Bug Repellents -Natural Homemade, Creams, Electronic & Reviews
- How do Bed Bugs Spread? Are they Contagious? How Fast/Easily from Person, Room or House?
- Best Bed Bug Sprays-DIY Homemade, Natural, Brand Reviews
- Flea Bites vs Bed Bug Bites + Differences & Pictures
- How to Prevent Bed Bugs-Bites while Sleeping at Home, School, Hotel & Travelling
- How to get rid of Bed Bugs on Clothes-Can they Live, Bite through or Travel on Laundry
- Fumigation for Bed Bugs-Cost & Preparation
- How to get Bed Bugs out of Carpet with Cleaner & Powder
- How Long do Bed Bugs Live Without Food, Host, Air, in Cold & After Spraying
- Bed Bug Rash on Skin, Pictures, Treatment, Allergy & Symptoms
- Where do Bed Bugs Hide and how to Find them
- Mosquito Bites vs Bed Bug Bites-What’ are the differences
- Identifying Bed Bug Eggs- How they look like, Images & destruction
- How do you know if you have Bed Bugs-Symptoms & Signs
- Bed Bug vs Spider Bites- Differences with Pictures
Sources
[1] https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/bedbugs/faqs.html
[2] https://www.orkin.com/other/bed-bugs/bedbugs-and-disease/
[3] https://www.pennmedicine.org/news/news-releases/2014/november/penn-study-shows-bed-bugs-can
[4] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2734207/