Table of Contents
Overview: Spiders & Bed Bugs
In the world, there are over 37,500 species of spiders. This number, when compared to the number of species of bed bugs is in the order of magnitudes.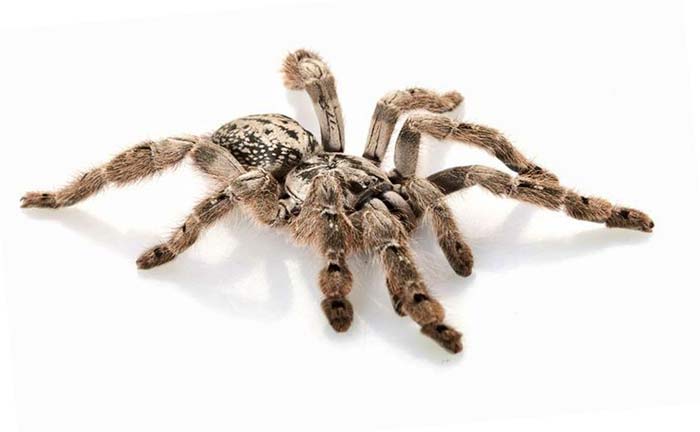
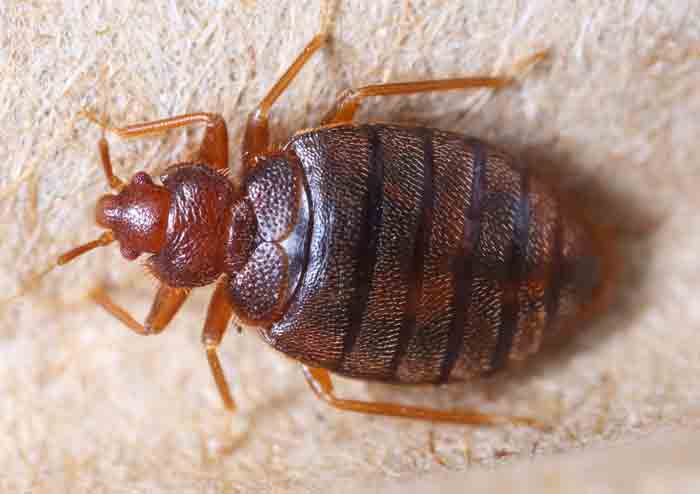

Appearance
The characteristic appearance of a spider bite can be categorized into the most common and rare appearances. The most common signs of regular spider bites include redness: as a normal inflammation would have it, the bite leads to an allergic reaction and it is common for redness to occur. In fact, even the rare bites start off as a red inflammation. The red is however bigger as compared to that of a bed bug which is quite small spanning a whole palm-surface area. More complicated and rare spider bites present differently with:- Bite marks: the black widow leaves a number of bites that bleed and resemble fangs. This means that they occur in pairs. Tarantulas also have the same features among other spiders with fangs. However, as compared to the Black Widow, tarantulas aren’t dangerously venomous. The bite marks are painful (Payne, K., Schilli, K., Meier, K., Rader, R., Dyer, J., & Mold, J. et al., 2014) and only become itchy as it scars during the healing process.
- Fluid discharge and blackening: hobo spiders are known to bite and cause reddening, swelling within an hour, discharge of fluid within 24 hours and eventually scarring in which the wound turns black
- Systemic signs: some of these signs that accompany a bite from Black Widow, Hobo Spider, Tarantula, Brazilian wandering spider and the Brown Recluse spider include: nausea, vomiting, rapid heart rate, hyperhidrosis, headache, visual disruption, and hypersalivating.
- The bites do not necessarily have to turn red in some skin complexions. If they do, they are contained and confined to small areas and are flat. They have no scarring or epicenter to the inflammation and appear in streaks that resemble lines more like welts.
- The bits appear in a succession of about 4-6 bites in a line.
- Bed bug bites tend to appear relatively faster as compared to spider bites. There are in fact spiders that numb the area for a whole 30 minutes after which there will be a swelling that may be itchy or painful.
Size
Spider bites range in size depending on the type of spider that has bitten you. There are small bites resembling those of a bed bug about 4-5 mm long and 1.5-3 mm wide. Other rare bites are much bigger almost sizing to the tip of the fingers. However, the inflammation will be much larger than that of a bed bug with some sizes sizing up to the surface of your palm.Disease Transmission
This is a question of whether spiders can carry bacteria and other pathogens that cause disease in humans. You can already rule out bed bugs from this as it has never been discovered to have such potential. They only feed on human blood but do not transmit any pathogen into the host as does lice, fleas, chiggers and ticks. Spiders can however provoke an infection as they lead to a breach of the skin. When the wounds are aggressively scratched or bleed, the pathogens on your skin may infect it and worsen it. In one study involving 182 Southern Californian patients with spider bites, findings were that less than 4% of the patients had envenomation and about 86% had skin infections. From the study, the Australian golden silk spider leads to an episode that results from a colonization of a rare bacterium, Photorhabdus luminescens that lasted about 2 months (Richard S. Vetter, David L. Swanson, Scott A. Weinstein, Julian White., 2015).Reaction
Reaction involved in both bed bug and spider bites are type 1 hypersensitivity reactions that are rather immediate. To this, itchiness and reddening of the affected area are common reactions. However, infections are delayed type reactions. Anaphylactic shock is common with some rare spider bites that are dangerously venomous.Identification
It is much easier to identify with the bite if a spider bit you as it may be utterly confusing. Remember that infections such as MRSA have the same presentation. Therefore, it will be quite in order if you saw the spider that bit you escape. However, it is easy to differentiate between a bed bug bite from a spider bite especially in the first few minutes during which bed bug bites fade away. However, if you are very sensitive to bed bub bites, they may be as big as spider bites and you will not notice and possibly even never get to known for even if it were a spider, its venom might only suffice a small allergy. Just look out for streaks and patterns to the bite to rule our spider bites.What and where they bite
Both bed bugs and spiders bite any place on your body they can gain access to. Bed bug bites are more superficial and only constrained to the epidermis as they are not equipped with fangs or long proboscis. Spiders have fangs but they are of different sizes. The medically important spiders are equipped with fangs that can lead to bleeding which means a breach of the superficial vasculature.Getting rid
Getting rid of spider or bed bug bites involves either conventional treatment or natural remedies. These options have been discussed in the following section under ‘Treatments’ to cap it all for both of these arthropods.Treatment
Treatment of bed bugs and spider bites are same as they are all allergic reactions. Special treatment and management will be instituted only when you have been bitten by the big four spiders that are considered very venomous and with systemic effects. For regular bites that are simple allergic reactions, you can use anti-inflammatory creams or ointments such as the corticosteroids. You can also get the oral antihistamines such as cetirizine or Chlopheniramine. There are medication that are a combination of the corticosteroids and the antihistamines such as betamethasone/dexchlopheniramine. The anti-histamines and the anti-inflammatories will still be used even in the management of rare spider bites. Additional care will involve management of any anaphylactic reactions such as shortness of breath, hives and wheezing in which you might consider an epinephrine injection or if not available, glucagon. This has to be done under supervision as an overdose of either could be catastrophic. Other methods may involve home remedies such as the application of lavender or peppermint oil. Unless the spider is known, a specific response to treatment may not be instigated. You should make a point of seeing the doctor when a seemingly medically insignificant bite from a bed bug turned complicated with shortness of breath, fever, general body malaise, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain among other systemic presentations.Prevention
Prevention of bed bugs involves the following: Bed bugs- Contact the professional pest service to treat your house if you have bed bugs.
- Wrap and dispose of any items that harbor bed bugs such as old furniture and mattresses.
- Use interceptors on the feet of your bed so that you can monitor any presence of bed bugs.
- When handling logs, firewood, boxes, wear something protective such as long-sleeved shirts, a cap, trousers, shoes and even gloves. Do so when you are cleaning basements and attics among other spider hideouts.
- Learn something about the spiders that are prevalent in your area or location and how to prevent and manage bites. Learn about their preferred habitat too.
- Before wearing clothing that has been stored for a long time, shake them out first.
- You can use, though not often, some Picaridin or DEET on your clothing and footwear to keep off spiders.
- Monitor your house for any cracks and broken windows and walls that may let in spiders. This is especially important if the area you live in is a known harbor of spiders among other insects.
- Use a vacuum to remove spider webs and spiders themselves.
Pictures
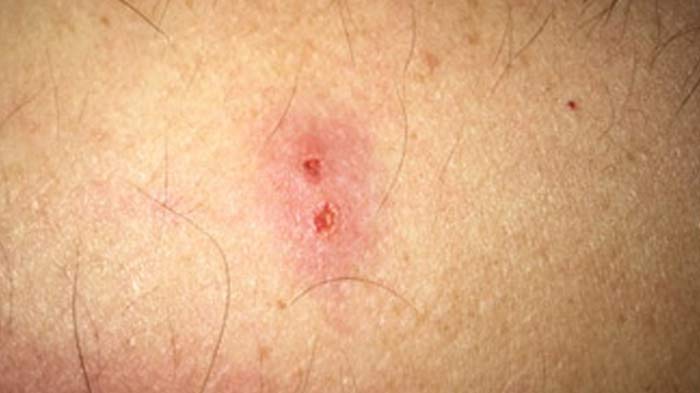
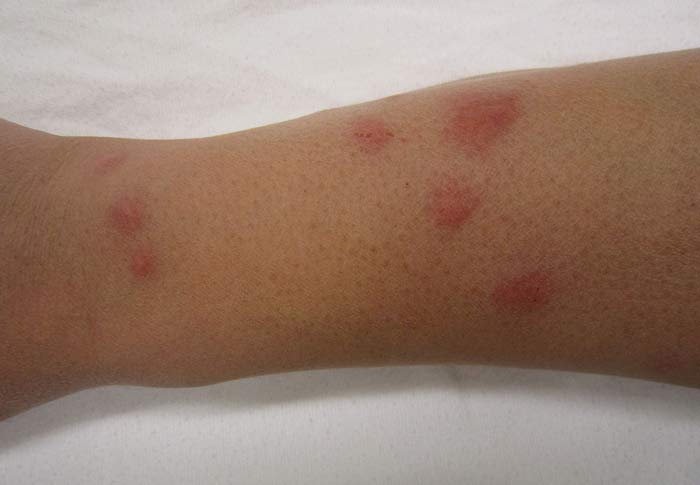
Similarities
Similarities between bed bug bites and spider bites lie in their ability to induce an allergic reaction that occurs as a red, swollen and itchy lesion. Not much similarity however. Further Reading- Bed Bug life cycle-Eggs, Baby(Nymph) to Adult Stages & Pictures
- How to Detect Bed Bugs-Detectors, Light & Verifi Reviews
- How to know if Bed Bugs are gone after Treatment & what to do
- Will Bleach Kill Bed Bugs-How does it work?
- Best Bed Bugs Traps- DIY Homemade, Co2, Yeast + Reviews
- How to Deal with Bed Bugs in your Car
- Bed Bugs in Couch-Covers, Signs & How to Get rid
- How to Kill Bed Bugs with Steam: Best Steamers & Guide + Tips
- Does Alcohol Kill Bed Bugs? Rubbing, Isopropyl & Percentage
- How Long do Bed Bug Bites Last, Take to Appear, Go Away & Heal
- Natural Predator of Bed Bugs-What Insects/Bugs eat Bed Bugs?
- Can Bed Bugs Live in TVs & Other Electronics? How to get them out
- Do Bed Bug Bites Itch or Hurt?
- Bed Bug Interceptor-How it works, DIY & Reviews
- What do Bed Bug Bites look like? Pictures & Identification Steps
- What Attracts Bed Bugs & things they Hate /Dislike Most
- Can Bed Bugs make you Sick? How are they Dangerous?
- Can Bed Bugs Fly-Do they have Wings-How Far can they Travel
- Diatomaceous Earth for Bed Bugs-How to Use & Best Reviews
- DIY Bed Bug Heat Treatment: Success Rate,Temperature Chart, Preparation & Reviews
- Does Vinegar Kill Bed Bugs? Can it be Used for Bites?
- How to Get Rid of Bed Bugs on Mattress- Best Covers, Protectors & Encasement Reviews
- Can Bed Bugs live on or Bite Dogs & Cats (Pets)?
- Bugs that look like Bed Bugs-Beetles & Others that Resemble or Mistaken
- Bed Bug Bombs-Do Foggers work? Effectiveness & Reviews
- Bed Bug Repellents -Natural Homemade, Creams, Electronic & Reviews
- How do Bed Bugs Spread? Are they Contagious? How Fast/Easily from Person, Room or House?
- Best Bed Bug Sprays-DIY Homemade, Natural, Brand Reviews
- Flea Bites vs Bed Bug Bites + Differences & Pictures
- How to Prevent Bed Bugs-Bites while Sleeping at Home, School, Hotel & Travelling
- How to get rid of Bed Bugs on Clothes-Can they Live, Bite through or Travel on Laundry
- Fumigation for Bed Bugs-Cost & Preparation
- How to get Bed Bugs out of Carpet with Cleaner & Powder
- How Long do Bed Bugs Live Without Food, Host, Air, in Cold & After Spraying
- Bed Bug Rash on Skin, Pictures, Treatment, Allergy & Symptoms
- Where do Bed Bugs Hide and how to Find them
- Mosquito Bites vs Bed Bug Bites-What’ are the differences
- Identifying Bed Bug Eggs- How they look like, Images & destruction
- How do you know if you have Bed Bugs-Symptoms & Signs
- Bed Bug vs Spider Bites- Differences with Pictures
- Bed Bug Sniffing Dogs-How they smell, Sense, Roscoe, Breeds & Cost
- What are Bed Bugs? Names in other Languages
- Where do Bed Bugs come from? Causes, how you get them & Start
- How to Kill/Get Rid of Bed Bugs Fast Yourself Naturally for Good
- Bed Bugs in Hair Symptoms, Pictures & Get rid
- Types of Bed Bugs
- Bed Bug Poop/Droppings-How it looks like, Pictures +Identification
- Bed Bug Shells, Cast Skin & Exoskeleton
- Can you See Bed Bugs with the Naked eye? Pictures, Size, Color & Anatomy
- Dust Mite vs Bed Bug Bites